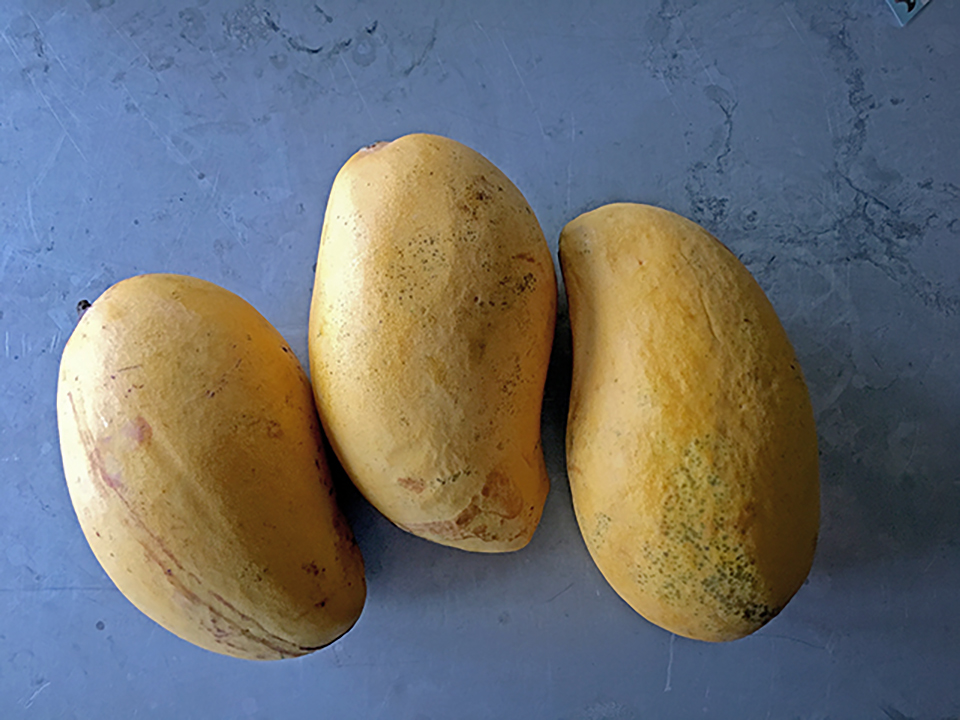Uncovering the facts about Ataulfo mango Latex staining & sap injury
This article was originally posted on Under the Mango Tree in February of 2017 and has been updated here.
Over the years, I really thought I understood the major problems affecting the “king of fruits,” specifically the varietals and those from the countries I worked with. Since I have traveled to orchards on multiple continents to examine the fruit and its “afflictions du jour,” I thought I had the facts straight on mango quality. Alas, since I met the Crespo family, I have come to discover that I had barely scratched the surface when it came to mango quality issues.
Like most everyone in the industry, I had to sift through a lot of misinformation about the quality of mangoes, but I tend to ask a lot of questions. And because I am me, I share the information I find. Under The Mango Tree’s goal has always been to get more accurate mango information to buyers, industry folks, and consumers. As we all struggle to compete in the complex agriculture world, this blog has been my attempt at being part of the solution. Talking about commodity imperfections is an important part of that process and an important part of commodity education.
Today I want to talk and share about the dark marks we see on many of the Ataulfo mangoes from time to time and most often from the ones that hail from the southern regions: Chiapas and Oaxaca. The good news in this particular affliction/imperfection is, that the mangoes ripen through the aesthetic imperfections, that tend to be more predominant when at the greener stage (when most of you receive the product), rather nicely and turn golden yellow without many blemishes (when the consumers see it). Harvesting and packhouse behaviors make a difference and so does talking about it.